
The Role of Technology in Smart Grids: Revolutionizing the Electricity Industry
The traditional electricity grid, which has remained relatively unchanged for decades, is undergoing a significant transformation with the integration of advanced technologies. The advent of smart grids has revolutionized the way electricity is generated, transmitted, distributed, and consumed. At the heart of this transformation is the role of technology, which has enabled the creation of a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable electricity system.
What are Smart Grids?
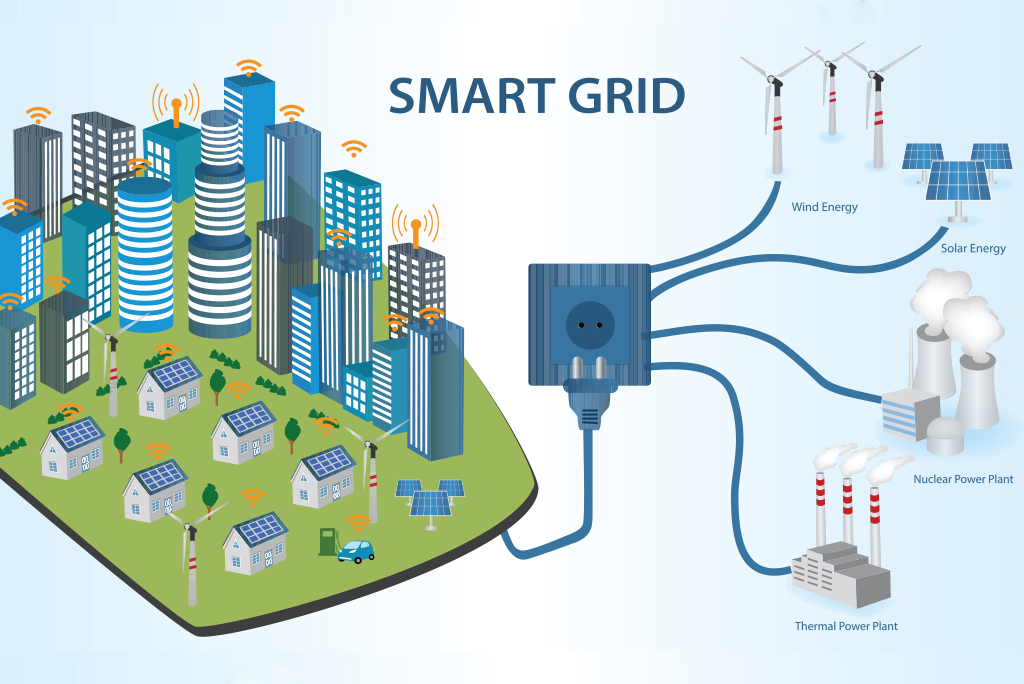
A smart grid is an advanced electrical grid that uses information and communication technologies (ICTs) to manage the generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption of electricity in a more efficient and sustainable way. It integrates traditional grid infrastructure with cutting-edge technologies such as automation, sensors, smart meters, and advanced data analytics to create a more intelligent and responsive system.
The Role of Technology in Smart Grids
Technology plays a crucial role in the development and operation of smart grids. Some of the key technologies driving the smart grid revolution include:
1. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
AMI is a critical component of smart grids, enabling the two-way communication between utilities and consumers. Smart meters, which are an integral part of AMI, provide real-time data on electricity consumption, allowing consumers to monitor their energy usage and adjust their behavior accordingly. Utilities can also use this data to optimize energy distribution, reduce peak demand, and improve grid efficiency.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT refers to the network of physical devices, sensors, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data. In the context of smart grids, IoT enables the integration of diverse devices and systems, facilitating real-time monitoring and control of grid operations.
3. Big Data Analytics
The massive amounts of data generated by smart grids require advanced data analytics capabilities to process, analyze, and interpret the information. Big data analytics enables utilities to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in energy consumption, predict energy demand, and optimize grid operations.
4. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides a scalable, flexible, and cost-effective platform for managing the vast amounts of data generated by smart grids. Utilities can leverage cloud-based services to store, process, and analyze data, reducing the need for on-premise infrastructure and improving grid efficiency.
5. Cybersecurity
As smart grids rely heavily on ICTs, cybersecurity is a critical concern. Advanced cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, are essential to protect the grid from cyber threats and ensure the reliability and integrity of the system.
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are being increasingly used in smart grids to analyze data, identify patterns, and make predictions. These technologies can help utilities optimize energy distribution, detect anomalies, and improve grid reliability.
Benefits of Technology in Smart Grids
The integration of advanced technologies in smart grids has numerous benefits, including:
1. Improved Efficiency
Smart grids enable utilities to optimize energy distribution, reduce energy losses, and improve grid efficiency. This leads to cost savings, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and improved customer satisfaction.
2. Enhanced Reliability
Advanced technologies, such as IoT and AI, enable real-time monitoring and control of grid operations, reducing the likelihood of power outages and improving grid reliability.
3. Increased Customer Engagement
Smart grids provide customers with real-time data on their energy consumption, enabling them to make informed decisions about their energy usage. This leads to increased customer engagement, energy conservation, and reduced peak demand.
4. Better Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Smart grids enable the seamless integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid. This leads to a more sustainable and diversified energy mix.
5. Improved Cybersecurity
Advanced cybersecurity measures protect the grid from cyber threats, ensuring the reliability and integrity of the system.
Challenges and Opportunities
While technology has revolutionized the electricity industry, there are challenges and opportunities associated with the adoption of smart grids:
1. Infrastructure Upgrades
The transition to smart grids requires significant infrastructure upgrades, including the installation of advanced metering infrastructure, IoT devices, and data analytics platforms.
2. Cybersecurity Concerns
The increased reliance on ICTs in smart grids raises cybersecurity concerns, requiring utilities to invest in advanced security measures to protect the grid.
3. Data Management
The massive amounts of data generated by smart grids require advanced data management capabilities, including data analytics, storage, and processing.
4. Grid Modernization
The transition to smart grids requires a fundamental transformation of the traditional grid infrastructure, including the integration of new technologies and business models.
5. Workforce Development
The adoption of smart grids requires utilities to upskill and reskill their workforce to manage and maintain the advanced technologies and systems.
Conclusion
The role of technology in smart grids is crucial, enabling the creation of a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable electricity system. Advanced technologies, such as AMI, IoT, big data analytics, cloud computing, cybersecurity, AI, and ML, are driving the smart grid revolution, providing numerous benefits to utilities, customers, and the environment. However, the adoption of smart grids also presents challenges and opportunities, requiring utilities to invest in infrastructure upgrades, cybersecurity measures, data management capabilities, and workforce development. As the electricity industry continues to evolve, the role of technology will remain critical, shaping the future of the smart grid.




